Appearance
树结构(Tree)
什么是树?
真实的树:
- 相信每个人对现实生活中的树都会非常熟悉
我们来看一下树有什么特点?
- 树通常有一个根。连接着根的是树干。
- 树干到上面之后会进行分叉成树枝,树枝还会分叉成更小的树枝。
- 在树枝的最后是叶子。
树的抽象:
- 专家们对树的结构进行了抽象,发现树可以模拟生活中的很多场景。

模拟树结构
公司组织架构: 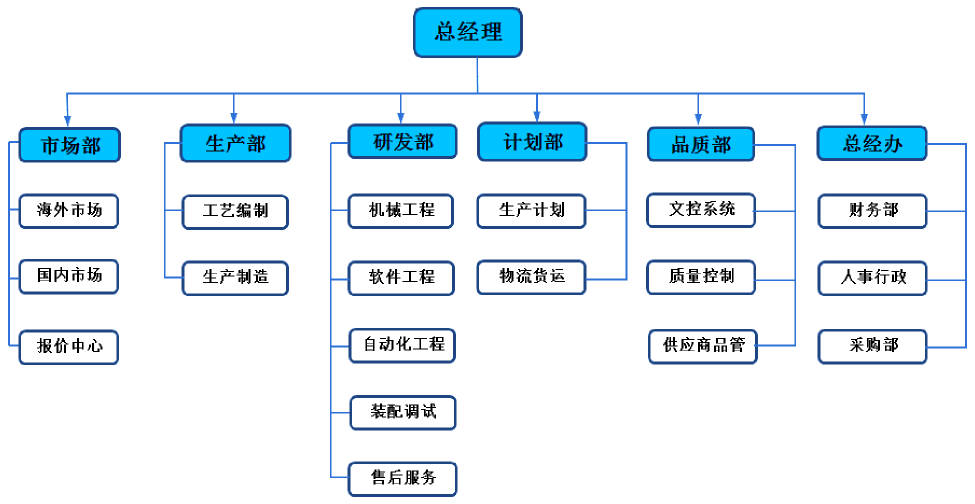 红楼梦家谱
红楼梦家谱 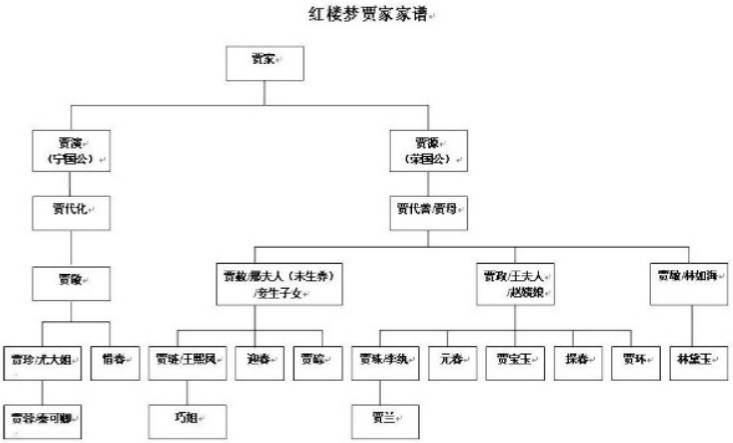
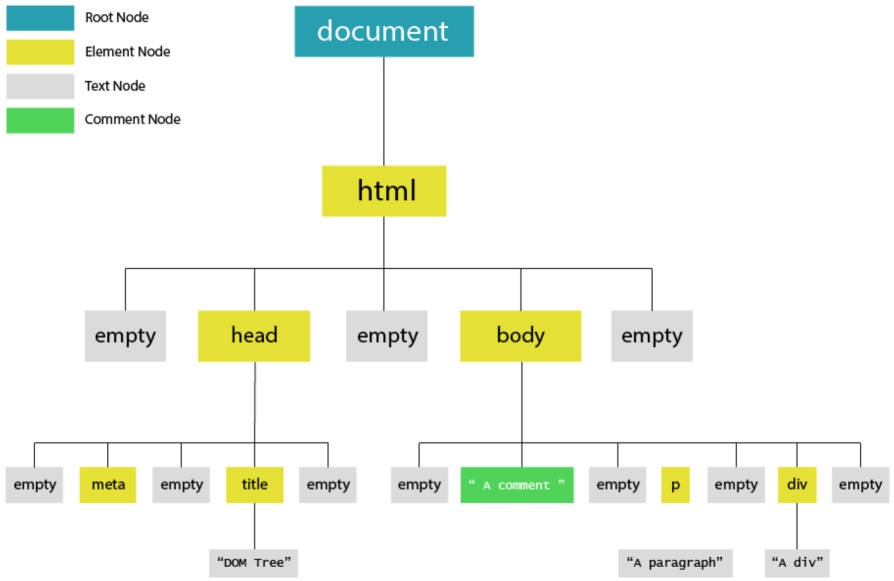
前端非常熟悉的 DOM Tree
树结构的抽象
我们再将里面的数据移除,仅仅抽象出来结构,那么就是我们要学习的树结构
树的优点
我们之前已经学习了多种数据结构来保存数据,为什么要使用树结构来保存数据呢?
树结构和数组/链表/哈希表的对比有什么优点呢?
数组:
优点:
- 数组的主要优点是根据下标值访问效率会很高。
- 但是如果我们希望根据元素来查找对应的位置呢?
- 比较好的方式是先对数组进行排序,再进行二分查找。
缺点:
- 需要先对数组进行排序,生成有序数组,才能提高查找效率。
- 另外数组在插入和删除数据时,需要有大量的位移操作(插入到首位或者中间位置的时候),效率很低。
链表:
优点:
- 链表的插入和删除操作效率都很高。
缺点:
- 查找效率很低,需要从头开始依次访问链表中的每个数据项,直到找到。
- 而且即使插入和删除操作效率很高,但是如果要插入和删除中间位置的数据,还是需要重头先找到对应的数据。
哈希表:
优点:
- 我们学过哈希表后,已经发现了哈希表的插入/查询/删除效率都是非常高的。
- 但是哈希表也有很多缺点。
缺点:
- 空间利用率不高,底层使用的是数组,并且某些单元是没有被利用的。
- 哈希表中的元素是无序的,不能按照固定的顺序来遍历哈希表中的元素。
- 不能快速的找出哈希表中的最大值或者最小值这些特殊的值。
树结构:
- 我们不能说树结构比其他结构都要好,因为每种数据结构都有自己特定的应用场景。
- 但是树确实也综合了上面的数据结构的优点(当然优点不足于盖过其他数据结构,比如效率一般情况下没有哈希表高)。
- 并且也弥补了上面数据结构的缺点。
而且为了模拟某些场景,我们使用树结构会更加方便。
- 因为数结构的非线性的,可以表示一对多的关系
- 比如文件的目录结构。
树的术语
在描述树的各个部分的时候有很多术语。
- 为了让介绍的内容更容易理解,需要知道一些树的术语。
- 不过大部分术语都与真实世界的树相关,或者和家庭关系相关(如父节点和子节点),所以它们比较容易理解。
树(Tree):n(n≥0)个节点构成的有限集合。
- 当 n=0 时,称为空树;
对于任一棵非空树(n> 0),它具备以下性质:
- 树中有一个称为“根(Root)”的特殊节点,用 r 表示;
- 其余节点可分为 m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集 T1,T2,..。,Tm,其中每个集合本身又是一棵树,称为原来树的“子树(SubTree)”
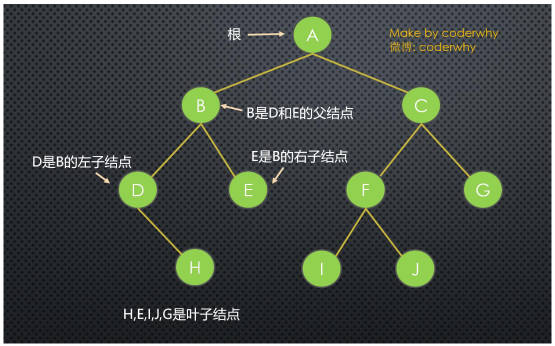
树的术语:
- 节点的度(Degree):节点的子树个数。
- 树的度 (Degree) :树的所有节点中最大的度数。
- 叶节点(Leaf):度为 0 的节点。(也称为叶子节点)
- 父节点(Parent):有子树的节点是其子树的根节点的父节点
- 子节点(Child):若 A 节点是 B 节点的父节点,则称 B 节点是 A 节点的子节点;子节点也称孩子节点。
- 兄弟节点(Sibling):具有同一父节点的各节点彼此是兄弟节点。
- 路径和路径长度:从节点 n1 到 nk 的路径为一个节点序列 n1 ,n2,… ,nk
- ni 是 n(i+1)的父节点
- 路径所包含 边 的个数为路径的长度。
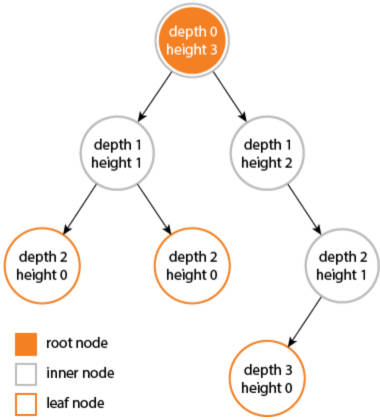
- 节点的层次(Level):规定根节点在 1 层,其它任一节点的层数是其父节点的层数加 1。
- 树的深度(Depth):对于任意节点 n, n 的深度为从根到 n 的唯一路径长,根的深度为 0。
- 树的高度(Height):对于任意节点 n,n 的高度为从 n 到一片树叶的最长路径长,所有树叶的高度为 0。
普通的表示方式
最普通的表示方式
儿子-兄弟表示法
儿子-兄弟表示法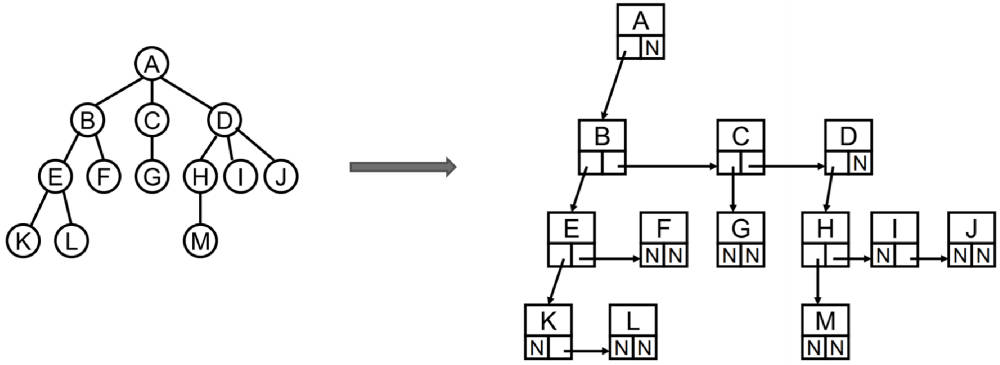
儿子-兄弟表示法旋转
儿子-兄弟表示法旋转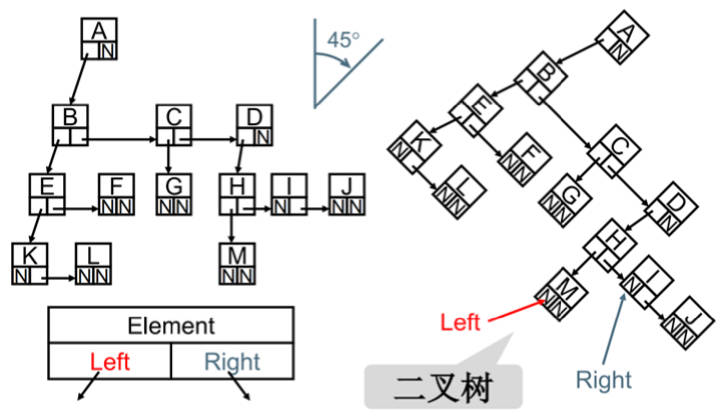
二叉树的概念
如果树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点,这样的树就成为"二叉树"。
- 前面,我们已经提过二叉树的重要性,不仅仅是因为简单,也因为几乎上所有的树都可以表示成二叉树的形式。
二叉树的定义
- 二叉树可以为空,也就是没有节点。
- 若不为空,则它是由根节点 和 称为其 左子树 TL 和 右子树 TR 的两个不相交的二叉树组成。
二叉树有五种形态: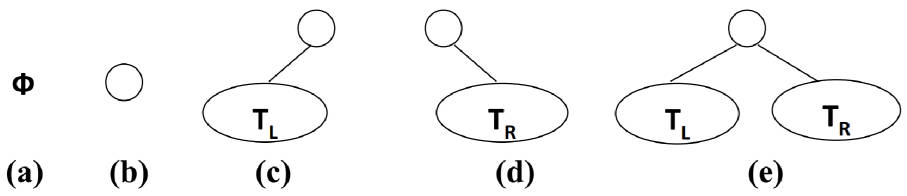
二叉树的特性
二叉树有几个比较重要的特性,在笔试题中比较常见:
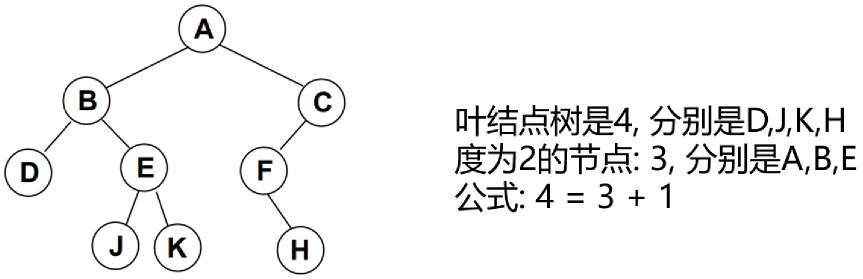
- 一颗二叉树第 i 层的最大节点数为:2^(i-1),i >= 1;
- 深度为 k 的二叉树有最大节点总数为: 2^k - 1,k >= 1;
- 对任何非空二叉树 T,若 n0 表示叶节点的个数、n2 是度为 2 的非叶节点个数,那么两者满足关系 n0 = n2 + 1。
完美二叉树
完美二叉树(Perfect Binary Tree) ,也称为满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)
- 在二叉树中,除了最下一层的叶节点外,每层节点都有 2 个子节点,就构成了满二叉树。
完全二叉树
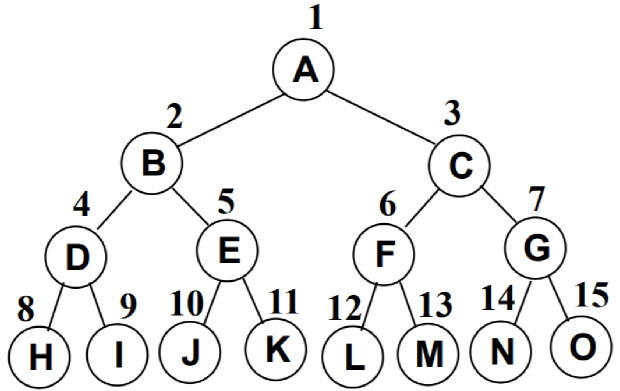
完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)
- 除二叉树最后一层外,其他各层的节点数都达到最大个数。
- 且最后一层从左向右的叶节点连续存在,只缺右侧若干节点。
- 完美二叉树是特殊的完全二叉树。
下面不是完全二叉树,因为 D 节点还没有右节点,但是 E 节点就有了左右节点。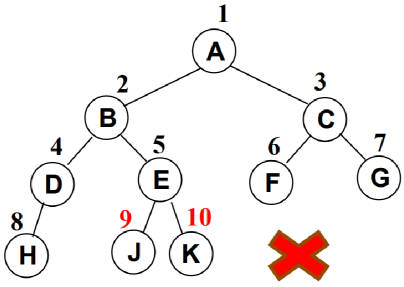
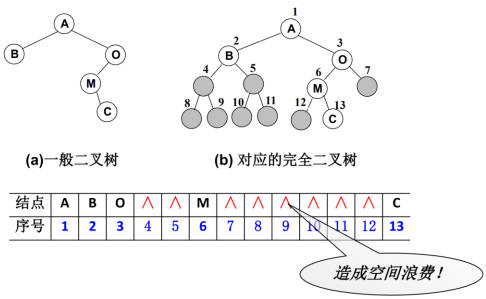
二叉树的存储
二叉树的存储常见的方式是数组和链表。使用数组
- 完全二叉树:按从上至下、从左到右顺序存储
非完全二叉树:
- 非完全二叉树要转成完全二叉树才可以按照上面的方案存储。
- 但是会造成很大的空间浪费
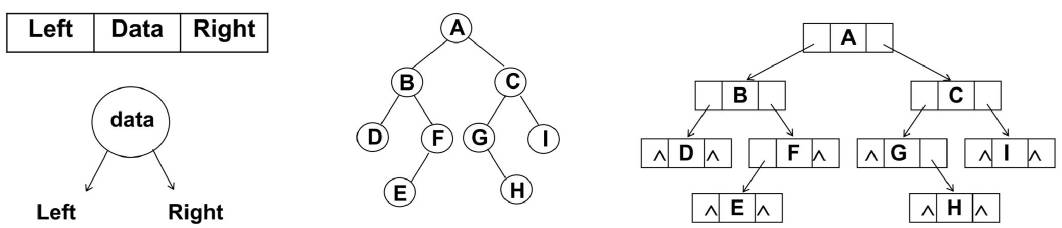
链表存储
二叉树最常见的方式还是使用链表存储。
- 每个节点封装成一个 Node,Node 中包含存储的数据,左节点的引用,右节点的引用。
什么是二叉搜索树?
二叉搜索树(BST,Binary Search Tree),也称二叉排序树或二叉查找树
二叉搜索树是一颗二叉树,可以为空;
如果不为空,满足以下性质:
- 非空左子树的所有键值小于其根节点的键值。
- 非空右子树的所有键值大于其根节点的键值。
- 左、右子树本身也都是二叉搜索树。
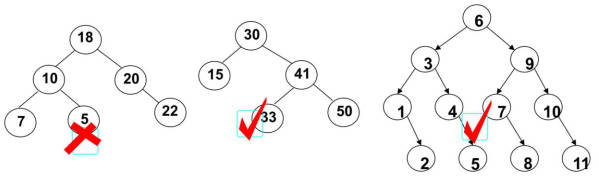
下面哪些是二叉搜索树,哪些不是?
二叉搜索树的特点:
- 二叉搜索树的特点就是相对较小的值总是保存在左节点上,相对较大的值总是保存在右节点上。
- 那么利用这个特点,我们可以做什么事情呢?
- 查找效率非常高,这也是二叉搜索树中,搜索的来源。
二叉搜索树
下面是一个二叉搜索树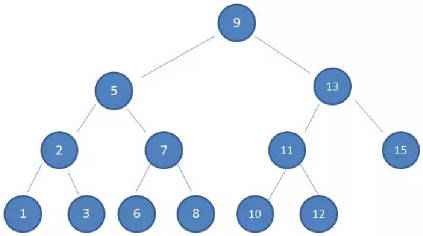
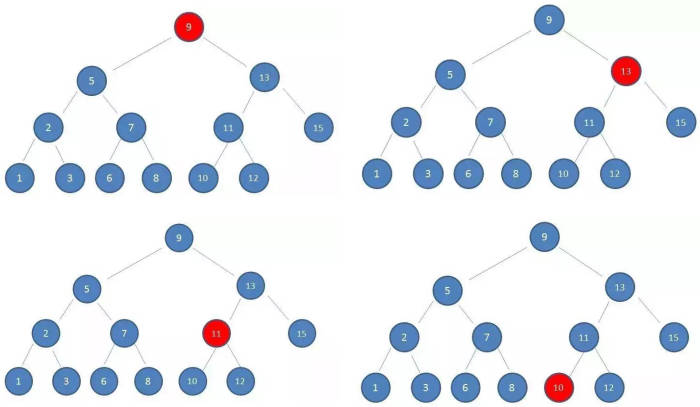
这样的数据结构有什么好处呢?
- 我们试着查找一下值为 10 的节点
这种方式就是二分查找的思想
- 查找所需的最大次数等于二叉搜索树的深度;
- 插入节点时,也利用类似的方法,一层层比较大小,找到新节点合适的位置。
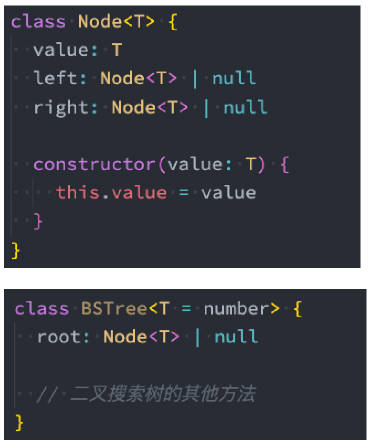
二叉搜索树的封装
我们像封装其他数据结构一样,先来封装一个 BSTree 的类
typescript
// types/Node.ts
class Node<T> {
value: T;
constructor(value: T) {
this.value = value;
}
}
export default Node;typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/01_二叉搜索树BSTree(封装).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
}
export {};代码解析:
- 封装 BSTree 的类;
- 还需要封装一个用于保存每一个节点的类 Node。
- 该类包含三个属性:节点对应的 value,指向的左子树 left,指向的右子树 right
- 对于 BSTree 来说,只需要保存根节点即可,因为其他节点都可以通过根节点找到。
二叉搜索树常见操作
二叉搜索树有哪些常见的操作呢?
插入操作:
- insert(value):向树中插入一个新的数据。
查找操作:
- search(value):在树中查找一个数据,如果节点存在,则返回 true;如果不存在,则返回 false。
- min:返回树中最小的值/数据。
- max:返回树中最大的值/数据。
遍历操作:
- inOrderTraverse:通过中序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
- preOrderTraverse:通过先序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
- postOrderTraverse:通过后序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
- levelOrderTraverse:通过层序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
删除操作(有一点点复杂):
- remove(value):从树中移除某个数据。
向树中插入数据
我们分两个部分来完成这个功能。
首先,外界调用的 insert 方法:
typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/02_二叉搜索树BSTree(插入).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (node.value >= newNode.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<number>();
bst.insert(11);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(13);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(18);
bst.insert(25);
bst.insert(6);
export {};代码解析:
首先,根据传入的 value,创建对应的 Node。
其次,向树中插入数据需要分成两种情况:
- 第一次插入,直接修改根节点即可。
- 其他次插入,需要进行相关的比较决定插入的位置。
在代码中的 insertNode 方法,我们还没有实现,也是我们接下来要完成的任务。
其次,插入非根节点
代码解析:
插入其他节点时,我们需要判断该值到底是插入到左边还是插入到右边。
判断的依据来自于新节点的 value 和原来节点的 value 值的比较。
- 如果新节点的 newvalue 小于原节点的 oldvalue,那么就向左边插入。
- 如果新节点的 newvalue 大于原节点的 oldvalue,那么就向右边插入。
代码的 1 序号位置,就是准备向左子树插入数据。但是它本身又分成两种情况
- 情况一(代码 1.1 位置):左子树上原来没有内容,那么直接插入即可。
- 情况二(代码 1.2 位置):左子树上已经有了内容,那么就一次向下继续查找新的走向,所以使用递归调用即可。
代码的 2 序号位置,和 1 序号位置几乎逻辑是相同的,只是是向右去查找。
- 情况一(代码 2.1 位置):左右树上原来没有内容,那么直接插入即可。
- 情况二(代码 2.2 位置):右子树上已经有了内容,那么就一次向下继续查找新的走向,所以使用递归调用即可。
测试插入代码
// 插入数据 bst.insert(11) bst.insert(7) bst.insert(15) bst.insert(5) bst.insert(3) bst.insert(9) bst.insert(8) bst.insert(10) bst.insert(13) bst.insert(12) bst.insert(14) bst.insert(20) bst.insert(18) bst.insert(25) bst.insert(6)
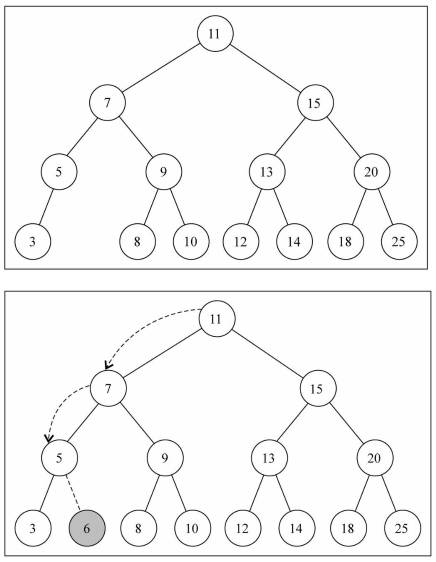
遍历二叉搜索树
前面,我们向树中插入了很多的数据,为了能很多的看到测试结果。我们先来学习一下树的遍历。
- 注意:这里我们学习的树的遍历,针对所有的二叉树都是适用的,不仅仅是二叉搜索树。
树的遍历:
- 遍历一棵树是指访问树的每个节点(也可以对每个节点进行某些操作,我们这里就是简单的打印)
- 但是树和线性结构不太一样,线性结构我们通常按照从前到后的顺序遍历,但是树呢?
- 应该从树的顶端还是底端开始呢? 从左开始还是从右开始呢?
二叉树的遍历常见的有四种方式:
- 先序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 层序遍历
先序遍历
遍历过程为:
- ① 访问根节点;
- ② 先序遍历其左子树;
- ③ 先序遍历其右子树。
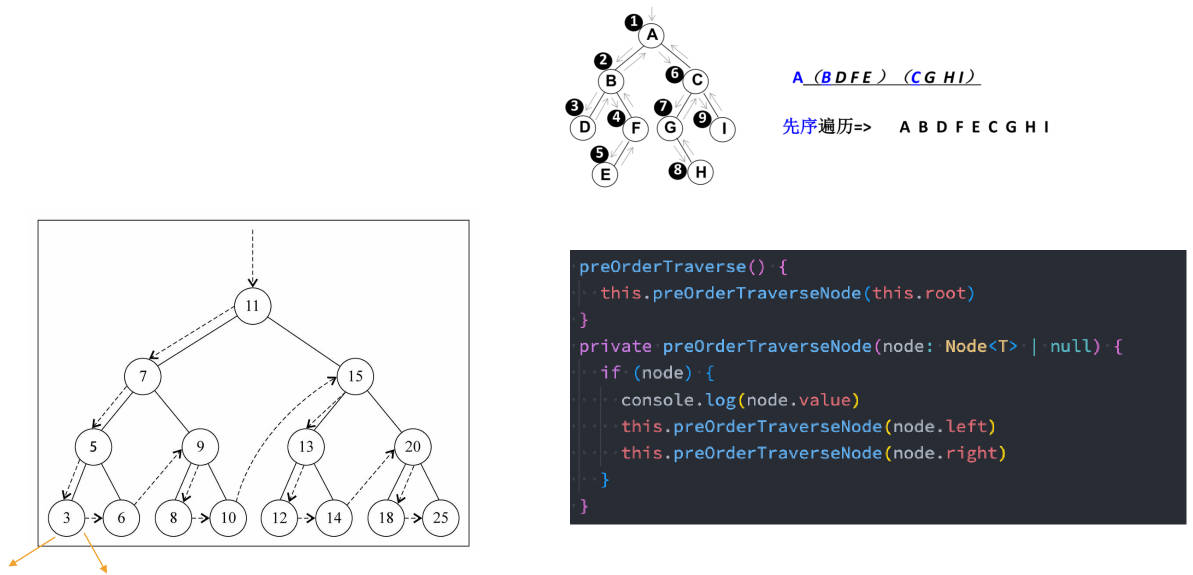
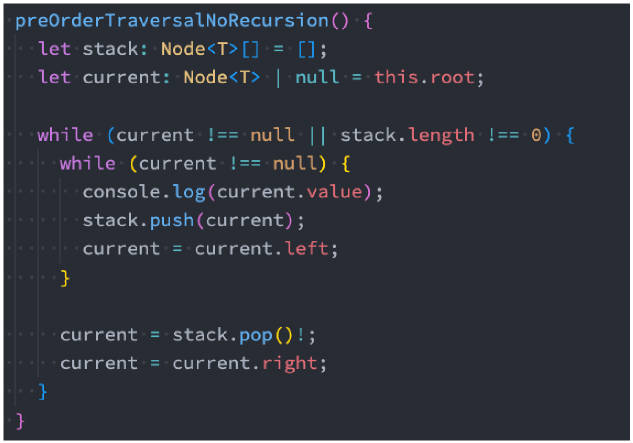
先序遍历(非递归 – 课下扩展)
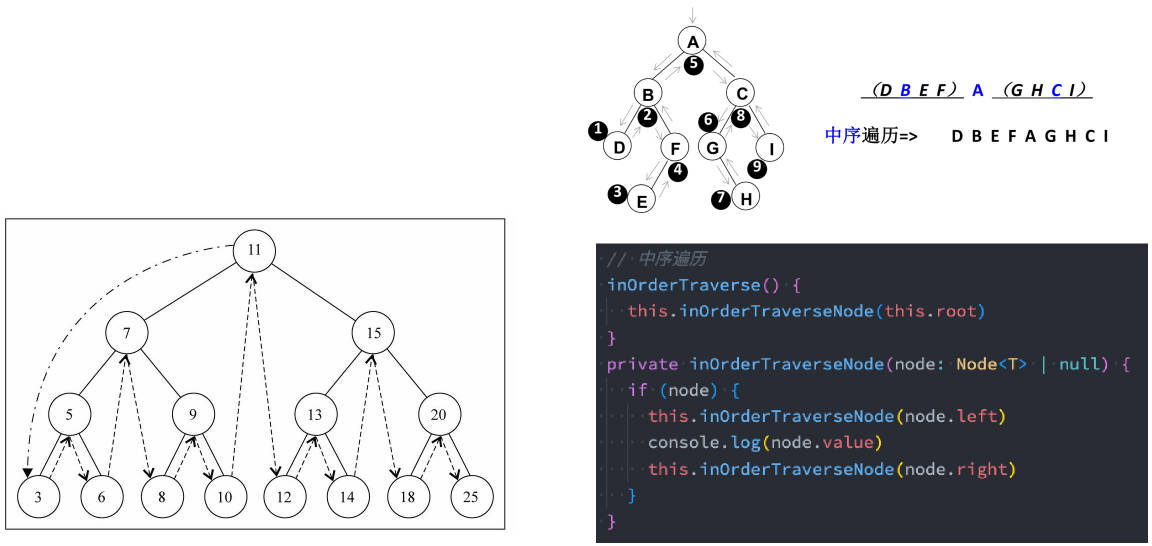
中序遍历
遍历过程为:
- ① 中序遍历其左子树;
- ② 访问根节点;
- ③ 中序遍历其右子树。
中序遍历(非递归 – 课下扩展)

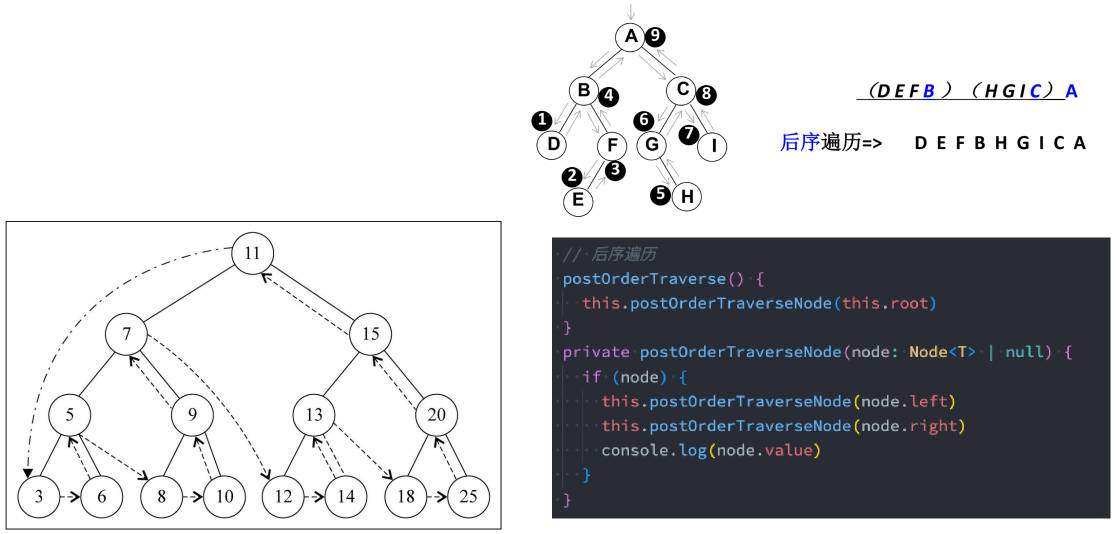
后序遍历
遍历过程为:
- ① 后序遍历其左子树;
- ② 后序遍历其右子树;
- ③ 访问根节点。
后序遍历(非递归 – 课下扩展)
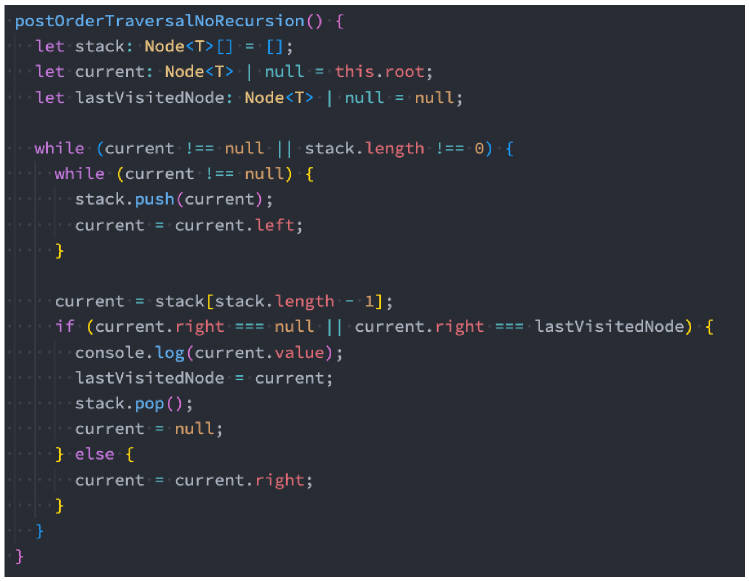
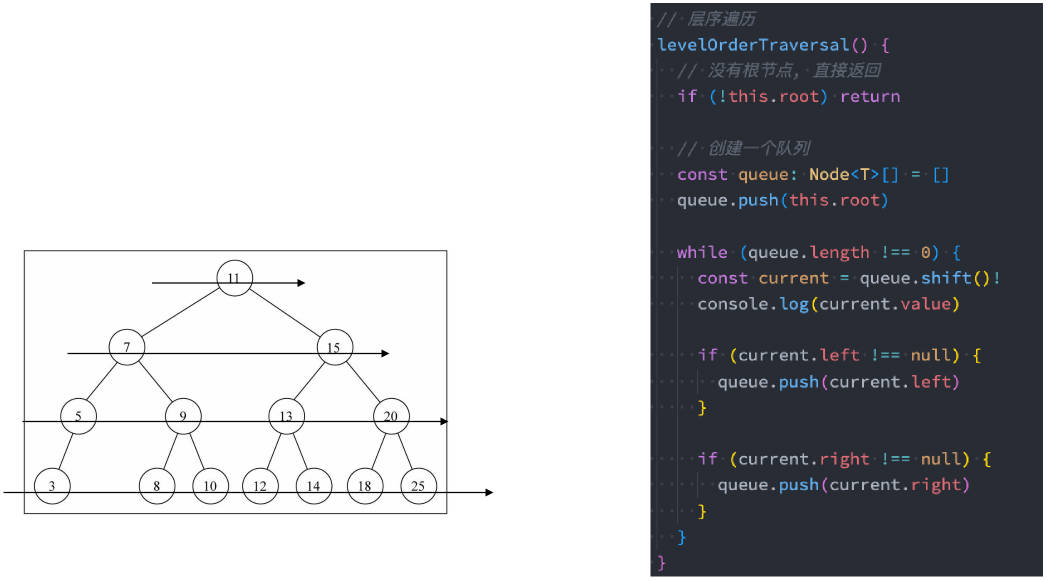
层序遍历
遍历过程为:
- 层序遍历很好理解,就是从上向下逐层遍历。
- 层序遍历通常我们会借助于队列来完成;
- ✓ 也是队列的一个经典应用场景;
- ✓ 也是队列的一个经典应用场景;
typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/03_二叉搜索树BSTree(遍历).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (node.value >= newNode.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/** 遍历的操作 */
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
console.log(node.value);
}
}
// 层次遍历
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点,那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return;
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = [];
// 第一个节点是根节点
queue.push(this.root);
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift();
console.log(current.value);
// 3.2.将左子节点放入到队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(root.left);
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(root.right);
}
}
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<number>();
bst.insert(11);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(13);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(18);
bst.insert(25);
bst.insert(6);
bst.preOrderTraverse();
bst.inOrderTraverse();
bst.postOrderTraverse();
bst.levelOrderTraverse();
export {};最大值 & 最小值
在二叉搜索树中搜索最值是一件非常简单的事情,其实用眼睛看就可以看出来了。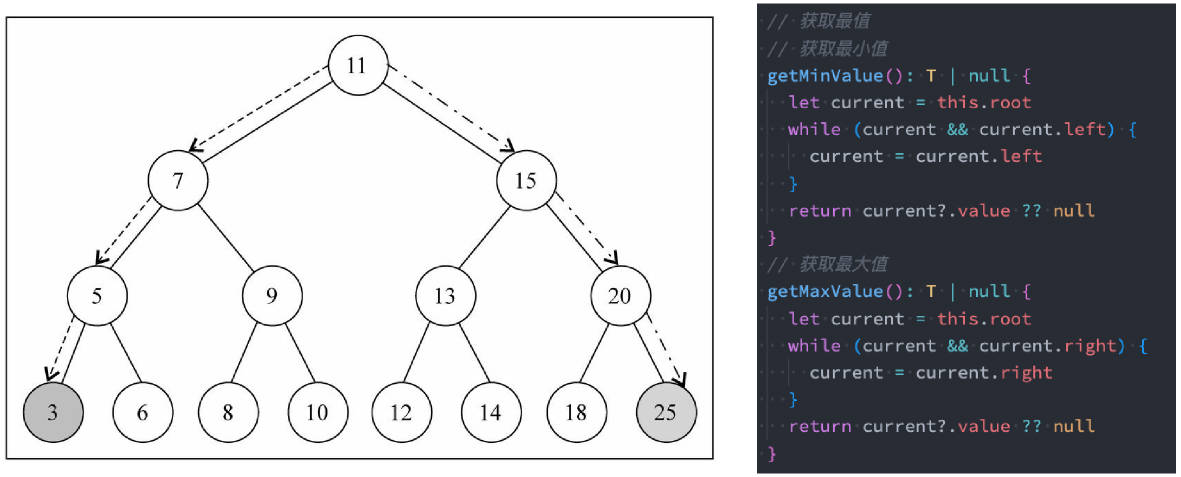
typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/04_二叉搜索树BSTree(最值).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (node.value >= newNode.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/** 遍历的操作 */
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
console.log(node.value);
}
}
// 层次遍历
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点,那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return;
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = [];
// 第一个节点是根节点
queue.push(this.root);
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift();
console.log(current.value);
// 3.2.将左子节点放入到队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(root.left);
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(root.right);
}
}
}
/** 获取最值操作:最大值/最小值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
getMinValue(): T | null {
const current = this.root;
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<number>();
bst.insert(11);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(13);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(18);
bst.insert(25);
bst.insert(6);
bst.preOrderTraverse();
bst.inOrderTraverse();
bst.postOrderTraverse();
bst.levelOrderTraverse();
export {};search 搜索特定的值
二叉搜索树不仅仅获取最值效率非常高,搜索特定的值效率也非常高。
- 注意:这里的实现返回 boolean 类型即可。
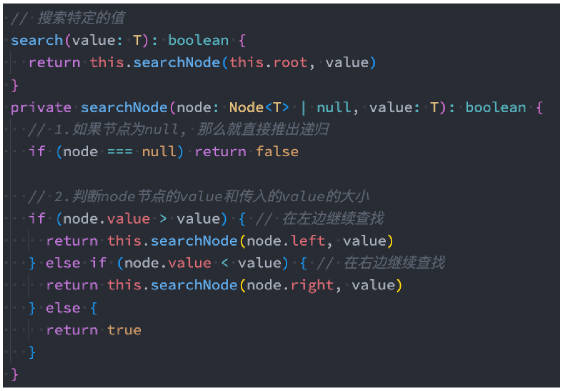
代码解析:
这里我们还是使用了递归的方式。
递归必须有退出条件,我们这里是两种情况下退出。
- node === null,也就是后面不再有节点的时候。
- 找到对应的 value,也就是 node.value === value 的时候。
在其他情况下,根据 node.的 value 和传入的 value 进行比较来决定向左还是向右查找。
- 如果 node.value > value,那么说明传入的值更小,需要向左查找。
- 如果 node.value < value,那么说明传入的值更大,需要向右查找。
search 搜索特定的值(非递归)
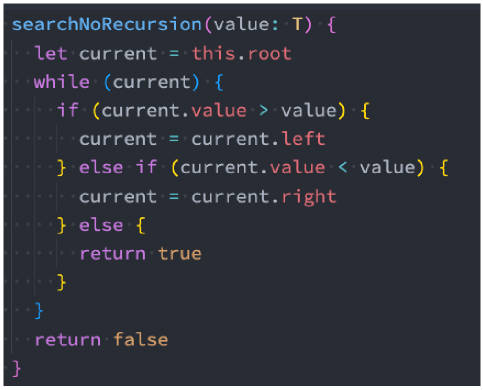
typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/05_二叉搜索树BSTree(搜索).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (node.value >= newNode.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/** 遍历的操作 */
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
console.log(node.value);
}
}
// 层次遍历
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点,那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return;
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = [];
// 第一个节点是根节点
queue.push(this.root);
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift();
console.log(current.value);
// 3.2.将左子节点放入到队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(root.left);
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(root.right);
}
}
}
/** 获取最值操作:最大值/最小值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
getMinValue(): T | null {
const current = this.root;
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
/** 搜索特点的值:20 => boolean */
search(value: T): boolean {
let current = this.root;
while (current) {
// 找到了节点
if (curren.value === value) return true;
if (current.value < value) {
current = current.right;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
}
return false;
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<number>();
bst.insert(11);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(13);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(18);
bst.insert(25);
bst.insert(6);
bst.print();
console.log(bst.search(20));
console.log(bst.search(18));
console.log(bst.search(6));
console.log(bst.search(30));
export {};二叉搜索树的删除
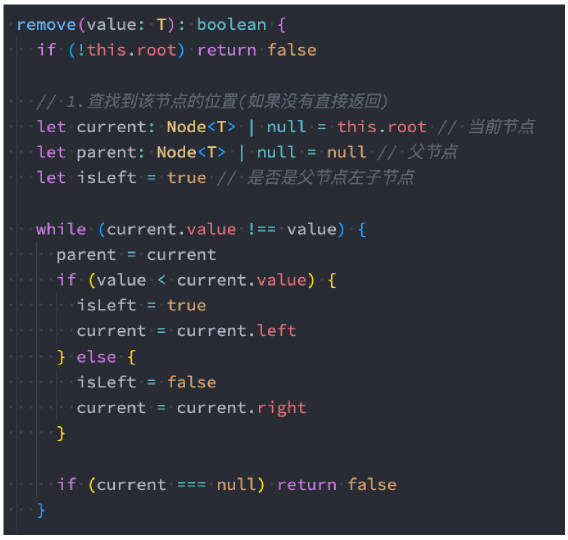
二叉搜索树的删除有些复杂,我们一点点完成。
删除节点要从查找要删的节点开始,找到节点后,需要考虑三种情况:
- 该节点是叶节点(没有子节点,比较简单)
- 该节点有一个子节点(也相对简单)
- 该节点有两个子节点.(情况比较复杂,我们后面慢慢道来)
我们先从查找要删除的节点入手
1> 先找到要删除的节点,如果没有找到,不需要删除
2> 找到要删除节点
- 1) 删除叶子节点
- 2) 删除只有一个子节点的节点
- 3) 删除有两个子节点的节点
情况一:没有子节点
情况一:没有子节点.
- 这种情况相对比较简单,我们需要检测 current 的 left 以及 right 是否都为 null.
- 都为 null 之后还要检测一个东西,就是是否 current 就是根,都为 null,并且为根,那么相当于要清空二叉树(当然,只是清空了根,因为只有它).
- 否则就把父节点的 left 或者 right 字段设置为 null 即可.
如果只有一个单独的根,直接删除即可
如果是叶节点,那么处理方式如下: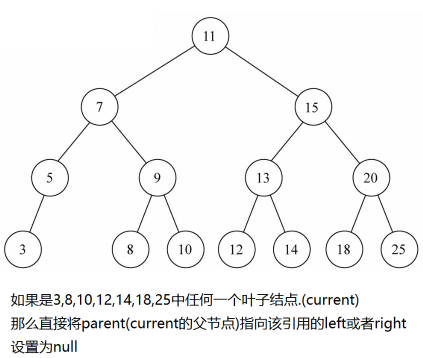
情况二:一个子节点
情况二:有一个子节点
- 这种情况也不是很难.
- 要删除的 current 节点,只有 2 个连接(如果有两个子节点,就是三个连接了),一个连接父节点,一个连接唯一的子节点.
- 需要从这三者之间:爷爷 - 自己 - 儿子,将自己(current)剪短,让爷爷直接连接儿子即可.
- 这个过程要求改变父节点的 left 或者 right,指向要删除节点的子节点.
- 当然,在这个过程中还要考虑是否 current 就是根.
图解过程:
- 如果是根的情况,大家可以自己画一下,比较简单,这里不再给出.
- 如果不是根,并且只有一个子节点的情况.

情况三:两个子节点
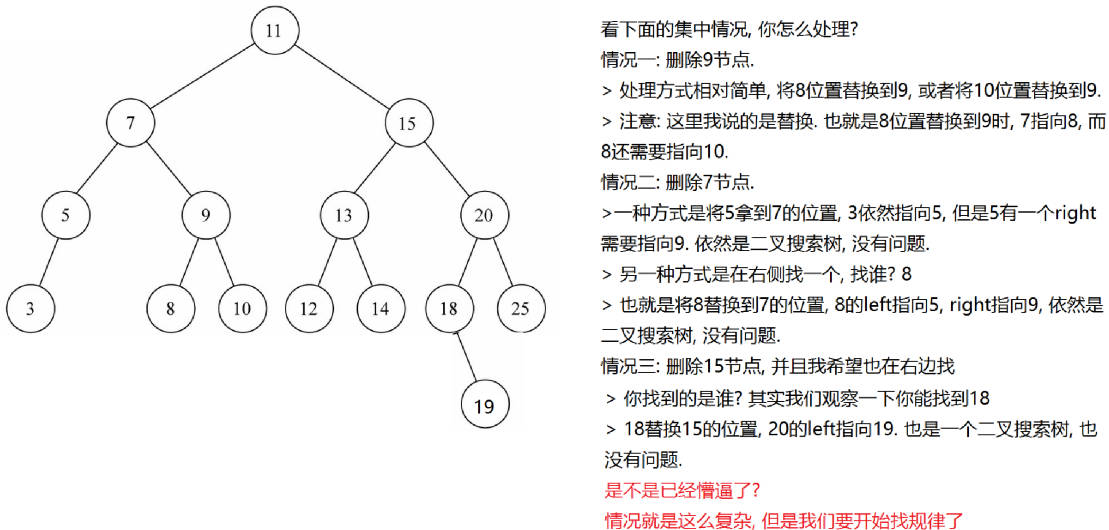
寻找规律
如果我们要删除的节点有两个子节点,甚至子节点还有子节点,这种情况下我们需要从下面的子节点中找到一个节点,来替换当前的节点.
但是找到的这个节点有什么特征呢? 应该是 current 节点下面所有节点中最接近 current 节点的.
- 要么比 current 节点小一点点,要么比 current 节点大一点点。
- 总之你最接近 current,你就可以用来替换 current 的位置.
这个节点怎么找呢?
- 比 current小一点点的节点,一定是 current左子树的最大值。
- 比 current大一点点的节点,一定是 current右子树的最小值。
前驱&后继
- 在二叉搜索树中,这两个特别的节点,有两个特别的名字。
- 比 current 小一点点的节点,称为 current 节点的前驱。
- 比 current 大一点点的节点,称为 current 节点的后继。
也就是为了能够删除有两个子节点的 current,要么找到它的前驱,要么找到它的后继。
所以,接下来,我们先找到这样的节点(前驱或者后继都可以,我这里以找后继为例)

typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/06_二叉搜索树BSTree(删除).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
import { btPrint } from "hy-algokit";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
// 当前节点的父节点
parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
// 判断当前节点是父节点的左子节点
get isLeft(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.left === this);
}
// 判断当前节点是父节点的右子节点
get isRight(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.right === this);
}
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
print() {
btPrint(this.root);
}
private searchNode(value: T): TreeNode<T> | null {
let current = this.root;
let parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
while (current) {
// 1.如果找到current, 直接返回即可
if (current.value === value) {
return current;
}
// 2.继续向下找
parent = current;
if (current.value < value) {
current = current.right;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
// 如果current有值, 那么current保存自己的父节点
if (current) current.parent = parent;
}
return null;
}
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (newNode.value < node.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/** 遍历的操作 */
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
console.log(node.value);
}
}
// 层序遍历
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点, 那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return;
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = [];
// 第一个节点时根节点
queue.push(this.root);
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift()!;
console.log(current.value);
// 3.2.将左子节点放入到队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left);
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right);
}
}
}
/** 获取最值操作: 最大值/最小值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
getMinValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
/** 搜索特定的值: 20 => boolean */
search(value: T): boolean {
return !!this.searchNode(value);
}
/** 实现删除操作 */
private getSuccessor(delNode: TreeNode<T>): TreeNode<T> {
// 获取右子树
let current = delNode.right;
let successor: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
while (current) {
successor = current;
current = current.left;
if (current) {
current.parent = successor;
}
}
// 拿到了后继节点
if (successor !== delNode.right) {
successor!.parent!.left = successor!.right;
successor!.right = delNode.right;
}
// 一定要进行的操作: 将删除节点的left, 赋值给后继节点的left
successor!.left = delNode.left;
return successor!;
}
remove(value: T): boolean {
// 1.搜索: 当前是否有这个value
const current = this.searchNode(value);
if (!current) return false;
// 2.获取到三个东西: 当前节点/父节点/是属于父节点的左子节点, 还是右子节点
// 2.如果删除的是叶子节点
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
if (current === this.root) {
// 根节点
this.root = null;
} else if (current.isLeft) {
// 父节点的左子节点
current.parent!.left = null;
} else {
current.parent!.right = null;
}
}
// 3.只有一个子节点: 只有左子节点
else if (current.right === null) {
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.left;
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = current.left;
} else {
current.parent!.right = current.left;
}
}
// 4.只有一个子节点: 只有右子节点
else if (current.left === null) {
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.right;
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = current.right;
} else {
current.parent!.right = current.right;
}
}
// 5.有两个子节点
else {
const successor = this.getSuccessor(current);
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = successor;
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = successor;
} else {
current.parent!.right = successor;
}
}
return true;
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<number>();
bst.insert(11);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(13);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(18);
bst.insert(25);
bst.insert(6);
bst.print();
// 删除功能: 删除有两个子节点的情况
bst.remove(11);
bst.print();
bst.remove(15);
bst.print();
bst.remove(9);
bst.print();
bst.remove(7);
bst.print();
export {};typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/06_二叉搜索树BSTree(删除-代码重构).ts
import Node from "../types/Node";
import { btPrint } from "hy-algokit";
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
// 当前节点的父节点
parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
// 判断当前节点是父节点的左子节点
get isLeft(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.left === this);
}
// 判断当前节点是父节点的右子节点
get isRight(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.right === this);
}
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
print() {
btPrint(this.root);
}
private searchNode(value: T): TreeNode<T> | null {
let current = this.root;
let parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
while (current) {
// 1.如果找到current, 直接返回即可
if (current.value === value) {
return current;
}
// 2.继续向下找
parent = current;
if (current.value < value) {
current = current.right;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
// 如果current有值, 那么current保存自己的父节点
if (current) current.parent = parent;
}
return null;
}
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (newNode.value < node.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/** 遍历的操作 */
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
console.log(node.value);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
console.log(node.value);
}
}
// 层序遍历
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点, 那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return;
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = [];
// 第一个节点时根节点
queue.push(this.root);
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift()!;
console.log(current.value);
// 3.2.将左子节点放入到队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left);
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right);
}
}
}
/** 获取最值操作: 最大值/最小值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
getMinValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current?.value ?? null;
}
/** 搜索特定的值: 20 => boolean */
search(value: T): boolean {
return !!this.searchNode(value);
}
/** 实现删除操作 */
private getSuccessor(delNode: TreeNode<T>): TreeNode<T> {
// 获取右子树
let current = delNode.right;
let successor: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
while (current) {
successor = current;
current = current.left;
if (current) {
current.parent = successor;
}
}
// 拿到了后继节点
if (successor !== delNode.right) {
successor!.parent!.left = successor!.right;
successor!.right = delNode.right;
}
// 一定要进行的操作: 将删除节点的left, 赋值给后继节点的left
successor!.left = delNode.left;
return successor!;
}
remove(value: T): boolean {
// 1.搜索: 当前是否有这个value
const current = this.searchNode(value);
if (!current) return false;
// 2.获取到三个东西: 当前节点/父节点/是属于父节点的左子节点, 还是右子节点
let replaceNode: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
replaceNode = null;
} else if (current.right === null) {
replaceNode = current.left;
} else if (current.left === null) {
replaceNode = current.right;
} else {
const successor = this.getSuccessor(current);
replaceNode = successor;
}
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = replaceNode;
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = replaceNode;
} else {
current.parent!.right = replaceNode;
}
return true;
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<number>();
bst.insert(11);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(13);
bst.insert(12);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(18);
bst.insert(25);
bst.insert(6);
bst.print();
// 删除功能: 删除有两个子节点的情况
bst.remove(11);
bst.print();
bst.remove(15);
bst.print();
bst.remove(9);
bst.print();
bst.remove(7);
bst.print();
export {};typescript
// 06_二叉搜索树BSTree/07_二叉搜索树BSTree(存放Product对象).ts
import { btPrint, PrintableNode } from "hy-algokit";
class Node<T> {
data: T;
constructor(value: T) {
this.data = value;
}
}
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> implements PrintableNode {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
// 当前节点的父节点
parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
// 判断当前节点是父节点的左子节点
get isLeft(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.left === this);
}
// 判断当前节点是父节点的右子节点
get isRight(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.right === this);
}
get value() {
const data = this.data as Product;
return `${data.name}-${data.price}`;
}
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
print() {
btPrint(this.root);
}
private searchNode(value: T): TreeNode<T> | null {
let current = this.root;
let parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
while (current) {
// 1.如果找到current, 直接返回即可
if (current.data === value) {
return current;
}
// 2.继续向下找
parent = current;
if (current.data < value) {
current = current.right;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
// 如果current有值, 那么current保存自己的父节点
if (current) current.parent = parent;
}
return null;
}
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (newNode.data < node.data) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
// node节点的左边已经是空白
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/** 遍历的操作 */
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.data);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
console.log(node.data);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root);
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right);
console.log(node.data);
}
}
// 层序遍历
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点, 那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return;
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = [];
// 第一个节点时根节点
queue.push(this.root);
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift()!;
console.log(current.data);
// 3.2.将左子节点放入到队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left);
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right);
}
}
}
/** 获取最值操作: 最大值/最小值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right;
}
return current?.data ?? null;
}
getMinValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root;
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current?.data ?? null;
}
/** 搜索特定的值: 20 => boolean */
search(value: T): boolean {
return !!this.searchNode(value);
}
/** 实现删除操作 */
private getSuccessor(delNode: TreeNode<T>): TreeNode<T> {
// 获取右子树
let current = delNode.right;
let successor: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
while (current) {
successor = current;
current = current.left;
if (current) {
current.parent = successor;
}
}
// 拿到了后继节点
if (successor !== delNode.right) {
successor!.parent!.left = successor!.right;
successor!.right = delNode.right;
}
// 一定要进行的操作: 将删除节点的left, 赋值给后继节点的left
successor!.left = delNode.left;
return successor!;
}
remove(value: T): boolean {
// 1.搜索: 当前是否有这个value
const current = this.searchNode(value);
if (!current) return false;
// 2.获取到三个东西: 当前节点/父节点/是属于父节点的左子节点, 还是右子节点
let replaceNode: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
replaceNode = null;
} else if (current.right === null) {
replaceNode = current.left;
} else if (current.left === null) {
replaceNode = current.right;
} else {
const successor = this.getSuccessor(current);
replaceNode = successor;
}
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = replaceNode;
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = replaceNode;
} else {
current.parent!.right = replaceNode;
}
return true;
}
}
class Product {
constructor(public name: string, public price: number) {}
valueOf() {
return this.price;
}
}
const bst = new BSTree<Product>();
const p1 = new Product("iPhone", 100);
const p2 = new Product("huawei", 120);
const p3 = new Product("xiaomi", 80);
const p4 = new Product("oppo", 90);
const p5 = new Product("vivo", 70);
bst.insert(p1);
bst.insert(p2);
bst.insert(p3);
bst.insert(p4);
bst.insert(p5);
bst.print();
export {};删除操作总结
看到这里,你就会发现删除节点相当棘手。 实际上,因为它非常复杂,一些程序员都尝试着避开删除操作。
- 他们的做法是在 Node 类中添加一个 boolean 的字段,比如名称为isDeleted。
- 要删除一个节点时,就将此字段设置为true。
- 其他操作,比如 find()在查找之前先判断这个节点是不是标记为删除。
- 这样相对比较简单,每次删除节点不会改变原有的树结构。
- 但是在二叉树的存储中,还保留着那些本该已经被删除掉的节点。
上面的做法看起来很聪明,其实是一种逃避。
- 这样会造成很大空间的浪费,特别是针对数据量较大的情况。
- 而且,作为程序员要学会通过这些复杂的操作,锻炼自己的逻辑。
二叉搜索树的缺陷
二叉搜索树作为数据存储的结构由重要的优势:
- 可以快速地找到给定关键字的数据项 并且可以快速地插入和删除数据项。
但是,二叉搜索树有一个很麻烦的问题:
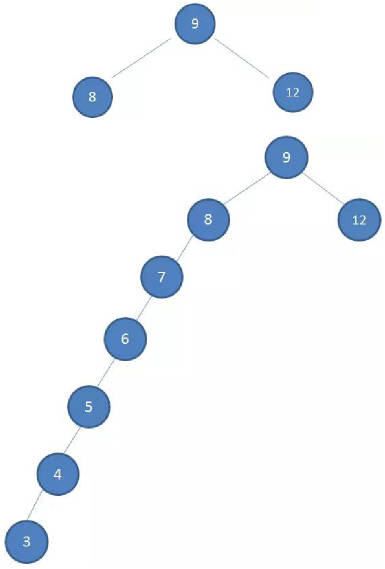
- 如果插入的数据是有序的数据,比如下面的情况
- 有一棵初始化为 9 8 12 的二叉树
- 插入下面的数据:7 6 5 4 3
非平衡树:
- 比较好的二叉搜索树数据应该是左右分布均匀的
- 但是插入连续数据后,分布的不均匀,我称这种树为非平衡树。
- 对于一棵平衡二叉树来说,插入/查找等操作的效率是O(logN)
- 对于一棵非平衡二叉树,相当于编写了一个链表,查找效率变成了O(N)
树的平衡性
为了能以较快的时间 O(logN)来操作一棵树,我们需要保证树总是平衡的:
- 至少大部分是平衡的,那么时间复杂度也是接近 O(logN)的
- 也就是说树中每个节点左边的子孙节点的个数,应该尽可能的等于右边的子孙节点的个数。
- 常见的平衡树有哪些呢?
AVL 树:
- AVL 树是最早的一种平衡树。它有些办法保持树的平衡(每个节点多存储了一个额外的数据)
- 因为 AVL 树是平衡的,所以时间复杂度也是 O(logN)。
- 但是,每次插入/删除操作相对于红黑树效率都不高,所以整体效率不如红黑树
红黑树:
- 红黑树也通过一些特性来保持树的平衡。
- 因为是平衡树,所以时间复杂度也是在 O(logN)。
- 另外插入/删除等操作,红黑树的性能要优于 AVL 树,所以现在平衡树的应用基本都是红黑树。
 阿金博客
阿金博客