Appearance
堆结构(Heap)
什么是堆(Heap)结构?
堆是也是一种非常常见的数据结构,但是相对于前面的数据结构来说,要稍微难理解一点。
堆的本质是一种特殊的树形数据结构,使用完全二叉树来实现:
- 堆可以进行很多分类,但是平时使用的基本都是二叉堆;
- 二叉堆又可以划分为最大堆和最小堆;
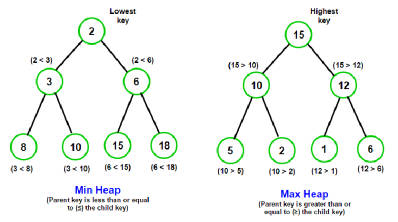
最大堆和最小堆:
- 最小堆:堆中每一个节点都小于等于(<=)它的子节点;
- 最大堆:堆中每一个节点都大于等于(>=)它的子节点;
为什么需要堆(Heap)结构?
但是这个堆东西有什么意义呢?
- 对于每一个新的数据结构,我们都需要搞清楚为什么需要它,这是我们能够记住并且把握它的关键。
- 它到底帮助我们解决了什么问题?
如果有一个集合,我们希望获取其中的最大值或者最小值,有哪些方案呢?
数组/链表:获取最大或最小值是 O(n)级别的;
✓ 可以进行排序,但是我们只是获取最大值或者最小值而已
✓ 排序本身就会消耗性能;
哈希表:不需要考虑了;
二叉搜索树:获取最大或最小值是 O(logn)级别的;
✓ 但是二叉搜索树操作较为复杂,并且还要维护树的平衡时才是 O(logn)级别;
这个时候需要一种数据结构来解决这个问题,就是堆结构。
认识堆(Heap)结构
堆结构通常是用来解决 Top K 问题的:
- Top K 问题是指在一组数据中,找出最前面的 K 个最大/最小的元素;
- 常用的解决方案有使用排序算法、快速选择算法、堆结构等;
但是我们还是不知道具体长什么样子,以及它是如何实现出来的:
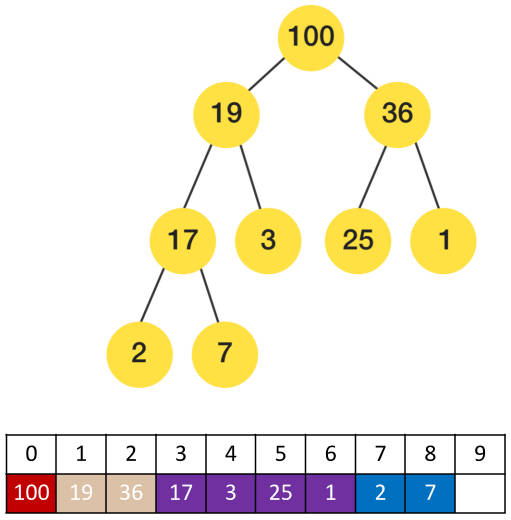
- 二叉堆用树形结构表示出来是一颗完全二叉树;
- 通常在实现的时候我们底层会使用数组来实现;
每个节点在数组中对应的索引 i(index)有如下的规律:
- 如果 i = 0 ,它是根节点;
- 父节点的公式:floor( (i – 1) / 2 )
- 左子节点:2i + 1
- 右子节点:2i + 2
堆结构的性质

堆结构的设计
接下来,让我们对堆结构进行设计,看看需要有哪些属性和方法。
常见的属性:
- data:存储堆中的元素,通常使用数组来实现。
- size:堆中当前元素的数量。
常见的方法:
- insert(value):在堆中插入一个新元素。
- extract/delete():从堆中删除最大/最小元素。
- peek():返回堆中的最大/最小元素。
- isEmpty():判断堆是否为空。
- build_heap(list):通过一个列表来构造堆。
那么接下来我们就来实现这个堆结构吧!
堆结构的封装
封装 Heap 的类: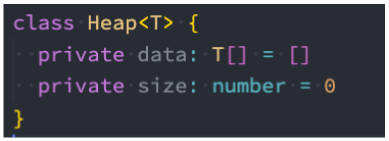
这个堆结构里面只包含了两个属性:data 和 size
- data是一个泛型数组,存储堆中的元素;
- size是当前堆中元素的数量。
typescript
// 09_堆结构HEAP/01_堆结构Heap(封装).ts
class Heap<T> {
// 属性
private data: T[] = [];
private length: number = 0;
// 私有工具方法
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
const temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}
// 方法
insert(value: T) {}
extract(): T | undefined {
return undefined;
}
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {}
}
export {};insert 插入元素
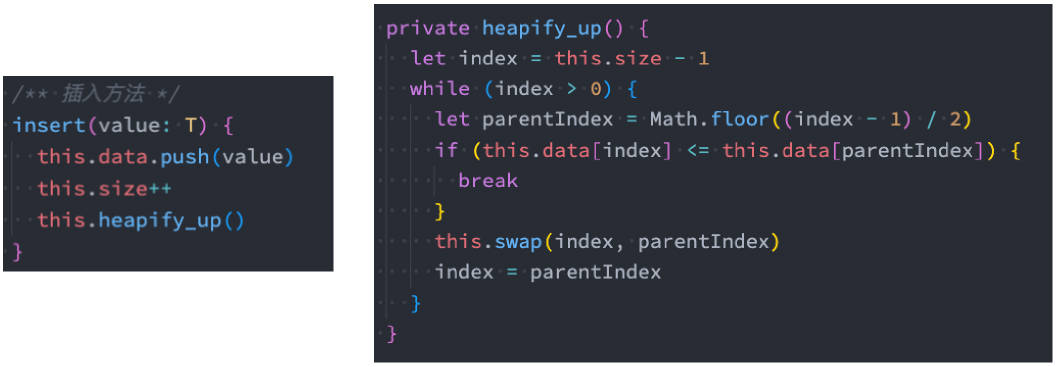
如果你想实现一个最大堆,那么可以从实现“insert”方法开始。
- 因为每次插入元素后,需要对堆进行重构,以维护最大堆的性质。
- 这种策略叫做上滤(percolate up, percolate [ˈpɜːkəleɪt] 是过滤的意思)。
数据模拟
typescript
// 09_堆结构HEAP/02_堆结构Heap(插入).ts
class Heap<T> {
// 属性
data: T[] = [];
private length: number = 0;
// 私有工具方法
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
const temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}
// 方法
insert(value: T) {
// 1.将元素放到数组的尾部
this.data.push(value);
this.length++;
// 2.维护最大堆的特性(最后位置的元素需要进行上滤操作)
this.heapify_up();
}
heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.data[index] <= this.data[parentIndex]) {
break;
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
extract(): T | undefined {
return undefined;
}
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {}
}
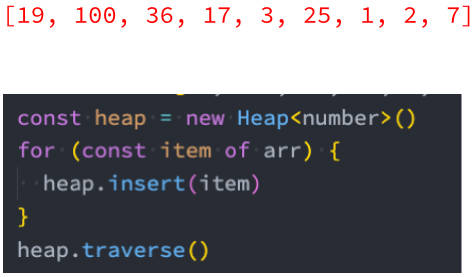
const arr = [19, 100, 36, 17, 3, 25, 1, 2, 7];
const heap = new Heap<number>();
for (const item of arr) {
heap.insert(item);
}
console.log(heap.data);
heap.insert(133);
console.log(heap.data);
heap.insert(65);
console.log(heap.data);
console.log(heap.extract());
export {};数据结构可视化
在线数据结构演练:
- https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html(加利福尼亚州的旧金山大学)
- https://visualgo.net/en/heap?slide=1
- http://btv.melezinek.cz/binary-heap.html
插入元素 insert
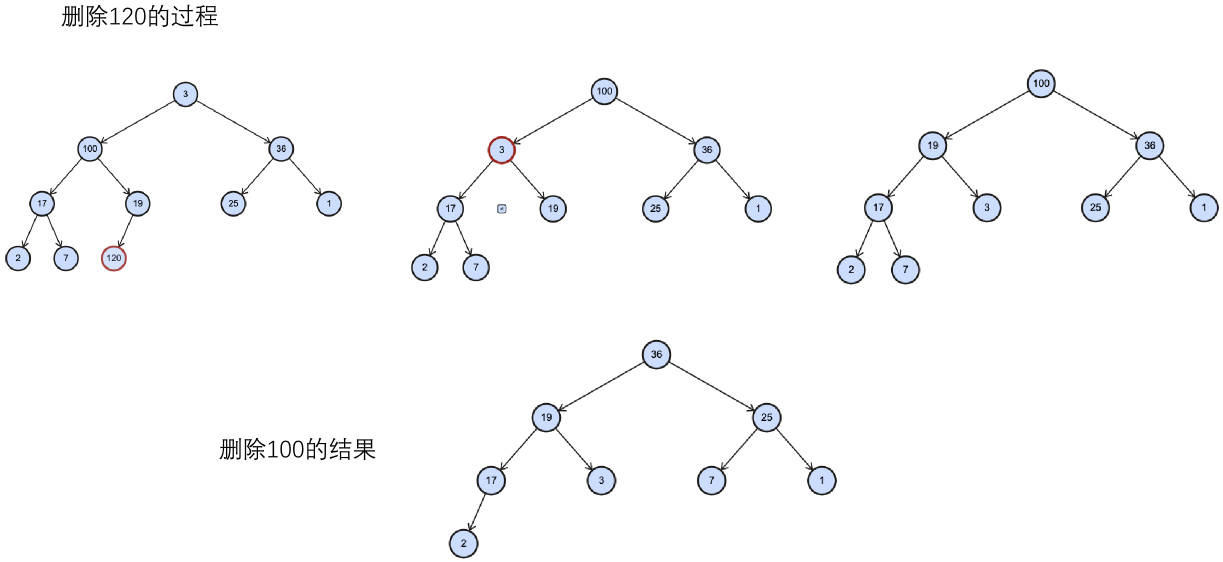
如果我们现在有这样一个结构的最大堆:插入 120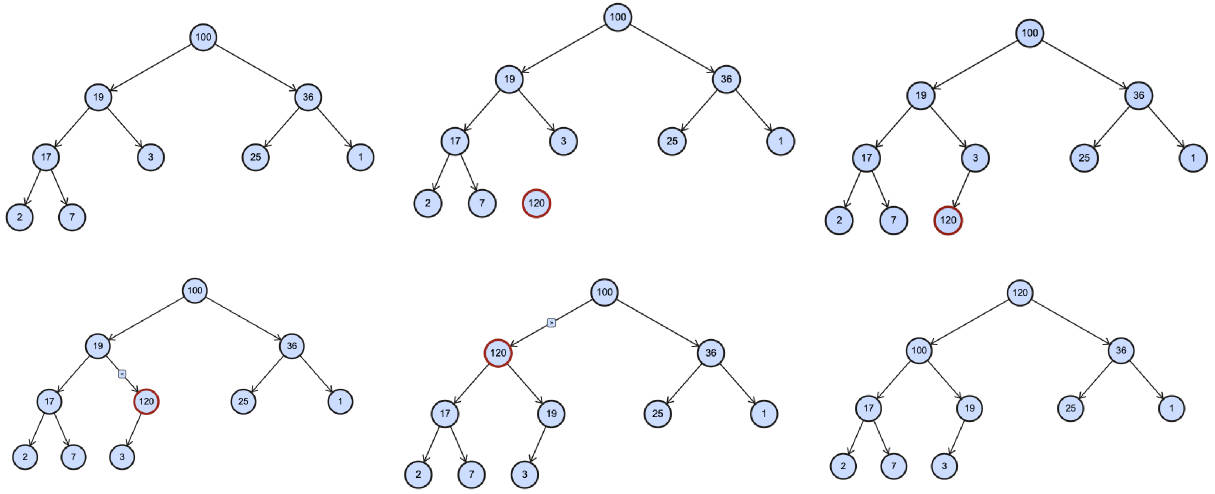
delete 删除元素
删除操作也需要考虑在删除元素后的操作:
- 因为每次删除元素后,需要对堆进行重构,以维护最大堆的性质。
- 这种向下替换元素的策略叫作下滤(percolate down)。
typescript
// 09_堆结构HEAP/03_堆结构Heap(删除).ts
class Heap<T> {
// 属性
data: T[] = [];
private length: number = 0;
// 私有工具方法
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
const temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}
// 方法
/** 插入操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.将元素放到数组的尾部
this.data.push(value);
this.length++;
// 2.维护最大堆的特性(最后位置的元素需要进行上滤操作)
this.heapify_up();
}
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.data[index] <= this.data[parentIndex]) {
break;
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
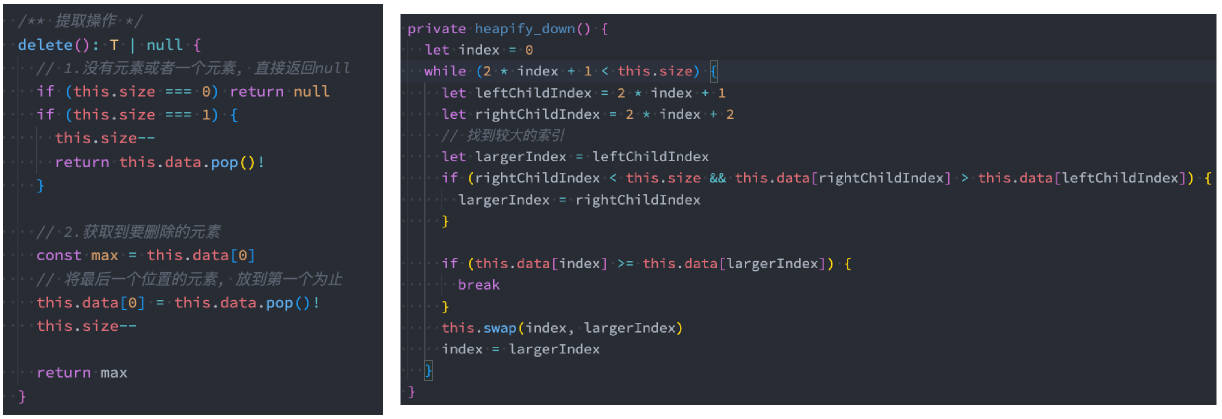
/** 提取操作 */
extract(): T | undefined {
// 1.判断元素的个数为0或者1的情况
if (this.length === 0) return undefined;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.length--;
return this.data.pop()!;
}
// 2.提取并且需要返回的最大值
const topValue = this.data[0];
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()!;
this.length--;
// 3.维护最大堆的特性: 下滤操作
this.heapify_down();
return topValue;
}
private heapify_down() {
// 3.1.定义索引位置
let index = 0;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
// 3.2.找到左右子节点
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1;
// 3.3.找到左右子节点较大的值
let largerIndex = leftChildIndex;
if (
rightChildIndex < this.length &&
this.data[rightChildIndex] > this.data[leftChildIndex]
) {
largerIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
// 3.4.较大的值和index位置进行比较
if (this.data[index] >= this.data[largerIndex]) {
break;
}
// 3.5.交换位置
this.swap(index, largerIndex);
index = largerIndex;
}
}
/** 其他方法 */
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {}
}
const arr = [19, 100, 36, 17, 3, 25, 1, 2, 7];
const heap = new Heap<number>();
for (const item of arr) {
heap.insert(item);
}
console.log(heap.data);
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
console.log(heap.extract());
}
export {};提取操作 extract、delete
其他方法的实现

原地建堆
“原地建堆” (In-place heap construction.)是指建立堆的过程中,不使用额外的内存空间,直接在原有数组上进行操作。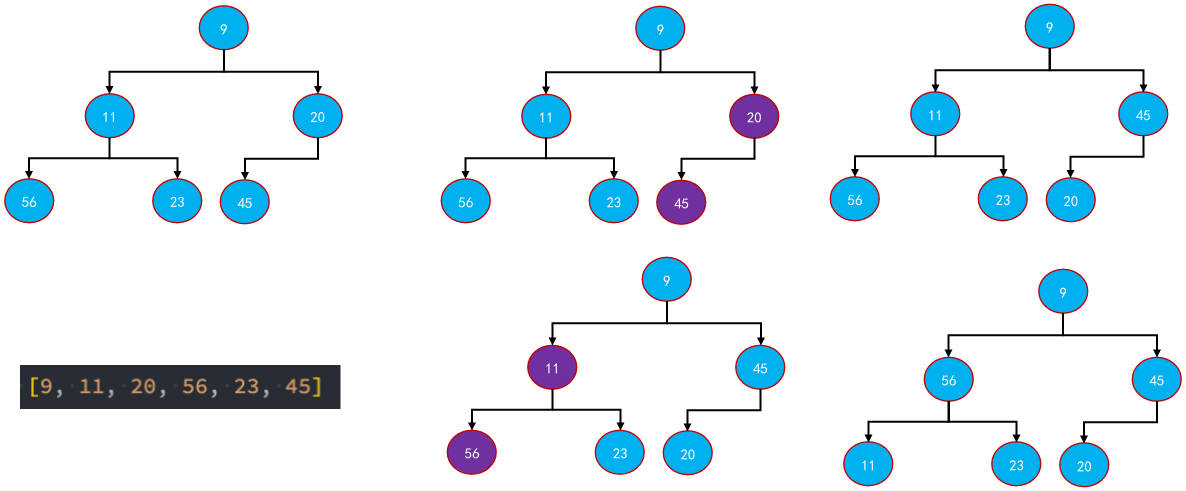
typescript
// 09_堆结构HEAP/04_堆结构Heap(原地建堆).ts
class Heap<T> {
// 属性
data: T[] = [];
private length: number = 0;
constructor(arr: T[] = []) {
this.buildHeap(arr);
}
// 私有工具方法
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
const temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}
// 方法
/** 插入操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.将元素放到数组的尾部
this.data.push(value);
this.length++;
// 2.维护最大堆的特性(最后位置的元素需要进行上滤操作)
this.heapify_up();
}
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.data[index] <= this.data[parentIndex]) {
break;
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
/** 提取操作 */
extract(): T | undefined {
// 1.判断元素的个数为0或者1的情况
if (this.length === 0) return undefined;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.length--;
return this.data.pop()!;
}
// 2.提取并且需要返回的最大值
const topValue = this.data[0];
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()!;
this.length--;
// 3.维护最大堆的特性: 下滤操作
this.heapify_down(0);
return topValue;
}
private heapify_down(start: number) {
// 3.1.定义索引位置
let index = start;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
// 3.2.找到左右子节点
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1;
// 3.3.找到左右子节点较大的值
let largerIndex = leftChildIndex;
if (
rightChildIndex < this.length &&
this.data[rightChildIndex] > this.data[leftChildIndex]
) {
largerIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
// 3.4.较大的值和index位置进行比较
if (this.data[index] >= this.data[largerIndex]) {
break;
}
// 3.5.交换位置
this.swap(index, largerIndex);
index = largerIndex;
}
}
/** 其他方法 */
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
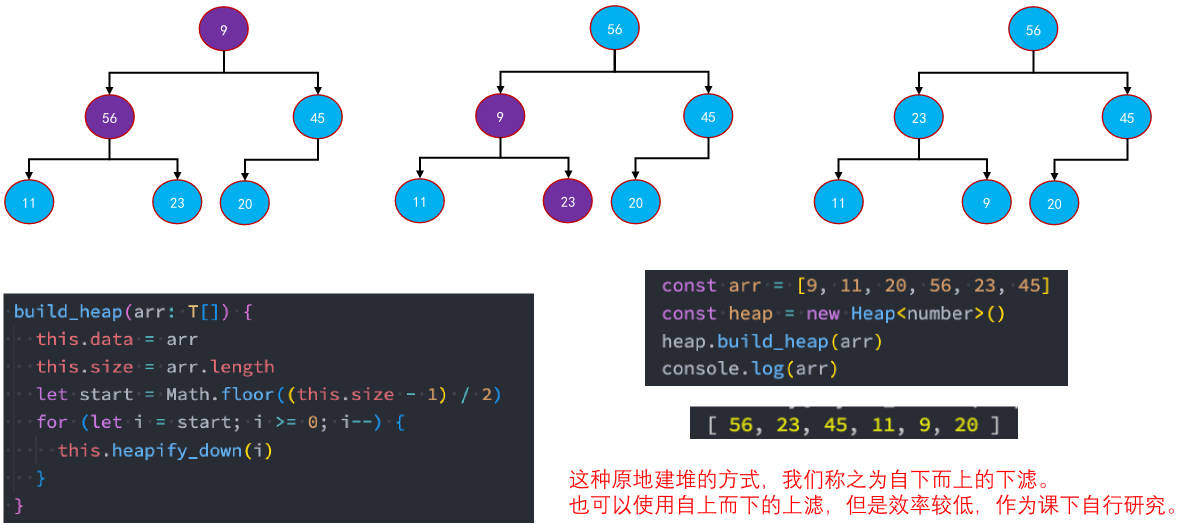
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {
// 1.使用arr的值: 数组/长度
this.data = arr;
this.length = arr.length;
// 2.从第一个非叶子节点, 开始进行下滤操作
const start = Math.floor(this.length / 2 - 1);
for (let i = start; i >= 0; i--) {
this.heapify_down(i);
}
}
}
const arr = [9, 11, 20, 56, 23, 45];
const heap = new Heap<number>(arr);
// heap.buildHeap(arr)
console.log(arr);
console.log(heap.extract());
export {};typescript
// 09_堆结构HEAP/05_堆结构Heap(最小堆).ts
class Heap<T> {
// 属性
data: T[] = [];
private length: number = 0;
constructor(arr: T[] = []) {
if (arr.length === 0) return;
this.buildHeap(arr);
}
// 私有工具方法
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
const temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}
// 方法
/** 插入操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.将元素放到数组的尾部
this.data.push(value);
this.length++;
// 2.维护最大堆的特性(最后位置的元素需要进行上滤操作)
this.heapify_up();
}
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.data[parentIndex] <= this.data[index]) {
break;
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
/** 提取操作 */
extract(): T | undefined {
// 1.判断元素的个数为0或者1的情况
if (this.length === 0) return undefined;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.length--;
return this.data.pop()!;
}
// 2.提取并且需要返回的最大值
const topValue = this.data[0];
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()!;
this.length--;
// 3.维护最大堆的特性: 下滤操作
this.heapify_down(0);
return topValue;
}
private heapify_down(start: number) {
// 3.1.定义索引位置
let index = start;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
// 3.2.找到左右子节点
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1;
// 3.3.找到左右子节点较大的值
let largerIndex = leftChildIndex;
if (
rightChildIndex < this.length &&
this.data[rightChildIndex] <= this.data[leftChildIndex]
) {
largerIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
// 3.4.较大的值和index位置进行比较
if (this.data[index] <= this.data[largerIndex]) {
break;
}
// 3.5.交换位置
this.swap(index, largerIndex);
index = largerIndex;
}
}
/** 其他方法 */
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {
// 1.使用arr的值: 数组/长度
this.data = arr;
this.length = arr.length;
// 2.从第一个非叶子节点, 开始进行下滤操作
const start = Math.floor((this.length - 1) / 2);
for (let i = start; i >= 0; i--) {
this.heapify_down(i);
}
}
}
const arr = [19, 100, 36, 17, 3, 25];
// 1.测试插入操作
// const heap = new Heap<number>()
// for (const item of arr) {
// heap.insert(item)
// }
// console.log(heap.data)
// 2.测试提取/删除操作
// while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
// console.log(heap.extract())
// }
// 3.测试批量建堆
const heap = new Heap<number>(arr);
console.log(arr);
console.log(heap.extract());
export {};typescript
// 09_堆结构HEAP/06_堆结构Heap(二叉堆).ts
import { cbtPrint } from "hy-algokit";
export default class Heap<T> {
// 属性
private data: T[] = [];
private length: number = 0;
private isMax: boolean;
constructor(arr: T[] = [], isMax = true) {
this.isMax = isMax;
if (arr.length === 0) return;
this.buildHeap(arr);
}
// 私有工具方法
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
const temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}
private compare(i: number, j: number): boolean {
if (this.isMax) {
return this.data[i] >= this.data[j];
} else {
return this.data[i] <= this.data[j];
}
}
// 方法
/** 插入操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.将元素放到数组的尾部
this.data.push(value);
this.length++;
// 2.维护最大堆的特性(最后位置的元素需要进行上滤操作)
this.heapify_up();
}
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.compare(parentIndex, index)) {
break;
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
/** 提取操作 */
extract(): T | undefined {
// 1.判断元素的个数为0或者1的情况
if (this.length === 0) return undefined;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.length--;
return this.data.pop()!;
}
// 2.提取并且需要返回的最大值
const topValue = this.data[0];
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()!;
this.length--;
// 3.维护最大堆的特性: 下滤操作
this.heapify_down(0);
return topValue;
}
private heapify_down(start: number) {
// 3.1.定义索引位置
let index = start;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
// 3.2.找到左右子节点
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1;
// 3.3.找到左右子节点较大的值
let largerIndex = leftChildIndex;
if (
rightChildIndex < this.length &&
this.compare(rightChildIndex, leftChildIndex)
) {
largerIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
// 3.4.较大的值和index位置进行比较
if (this.compare(index, largerIndex)) {
break;
}
// 3.5.交换位置
this.swap(index, largerIndex);
index = largerIndex;
}
}
/** 其他方法 */
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {
// 1.使用arr的值: 数组/长度
this.data = arr;
this.length = arr.length;
// 2.从第一个非叶子节点, 开始进行下滤操作
const start = Math.floor((this.length - 1) / 2);
for (let i = start; i >= 0; i--) {
this.heapify_down(i);
}
}
print() {
cbtPrint(this.data);
}
}
const arr = [19, 100, 36, 17, 3, 25];
// 1.测试插入操作
// const heap = new Heap<number>([], false)
// for (const item of arr) {
// heap.insert(item)
// }
// console.log(heap.data)
// // 2.测试提取/删除操作
// while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
// console.log(heap.extract())
// }
// 3.测试批量建堆
const heap = new Heap<number>(arr, false);
// console.log(arr)
// cbtPrint(arr)
// console.log(heap.extract())
// heap.print()
export {}; 阿金博客
阿金博客